5. Deploy Application
In part five of this tutorial, you will deploy the Todo List Application to the Environment.
Model the Todo List Application
Create a file called app.bicep in your current directory. This file defines all the resources that make up the Todo List Application, including how those resources are connected to each other.
Add the following to app.bicep:
extension radius
extension radiusResources
The extension radius statement imports the resource types built into Radius.
The extension radiusResources statement imports the PostgreSQL resource type created in the previous step.
@description('The ID of your Radius Environment. Set automatically by the rad CLI.')
param environment string
The environment parameter is set by the Radius CLI when deploying the application.
Add the Application resource
The Application resource is the parent resource for all other resources.
resource todolist 'Applications.Core/applications@2023-10-01-preview' = {
name: 'todolist'
properties: {
environment: environment
}
}
Add the PostgreSQL resource
Notice the size parameter is set by the developer to ‘S’.
resource postgresql 'Radius.Data/postgreSqlDatabases@2025-08-01-preview' = {
name: 'postgresql'
properties: {
environment: environment
application: todolist.id
size: 'S'
}
}
Add the Container resource
resource frontend 'Applications.Core/containers@2023-10-01-preview' = {
name: 'frontend'
properties: {
application: todolist.id
container: {
image: 'ghcr.io/radius-project/samples/demo:latest'
ports: {
web: {
containerPort: 3000
}
}
}
connections: {
postgresql: {
source: postgresql.id
}
}
}
}
When a connection is added between a container and another resource, the properties of the connected resource are created as environment variables in the container.
Deploy the application
Deploy the application using rad deploy.
rad deploy app.bicep
You should see output similar to:
Building app.bicep...
Deploying template 'app.bicep' for application 'todolist' and environment '/planes/radius/local/resourceGroups/my-group/providers/applications.core/environments/my-env' from workspace 'my-workspace'...
Deployment In Progress...
Completed todolist Applications.Core/applications
Completed postgresql Radius.Data/postgreSqlDatabases
Completed frontend Applications.Core/containers
Deployment Complete
Resources:
todolist Applications.Core/applications
frontend Applications.Core/containers
postgresql Radius.Data/postgreSqlDatabases
Set up port forwarding to access the Todo List Application using the rad resource expose command.
rad resource expose Applications.Core/containers frontend -a todolist --port 3000
Navigate to the http://localhost:3000 to access the Todo List application. You should see the Todo List application similar to this screenshot:
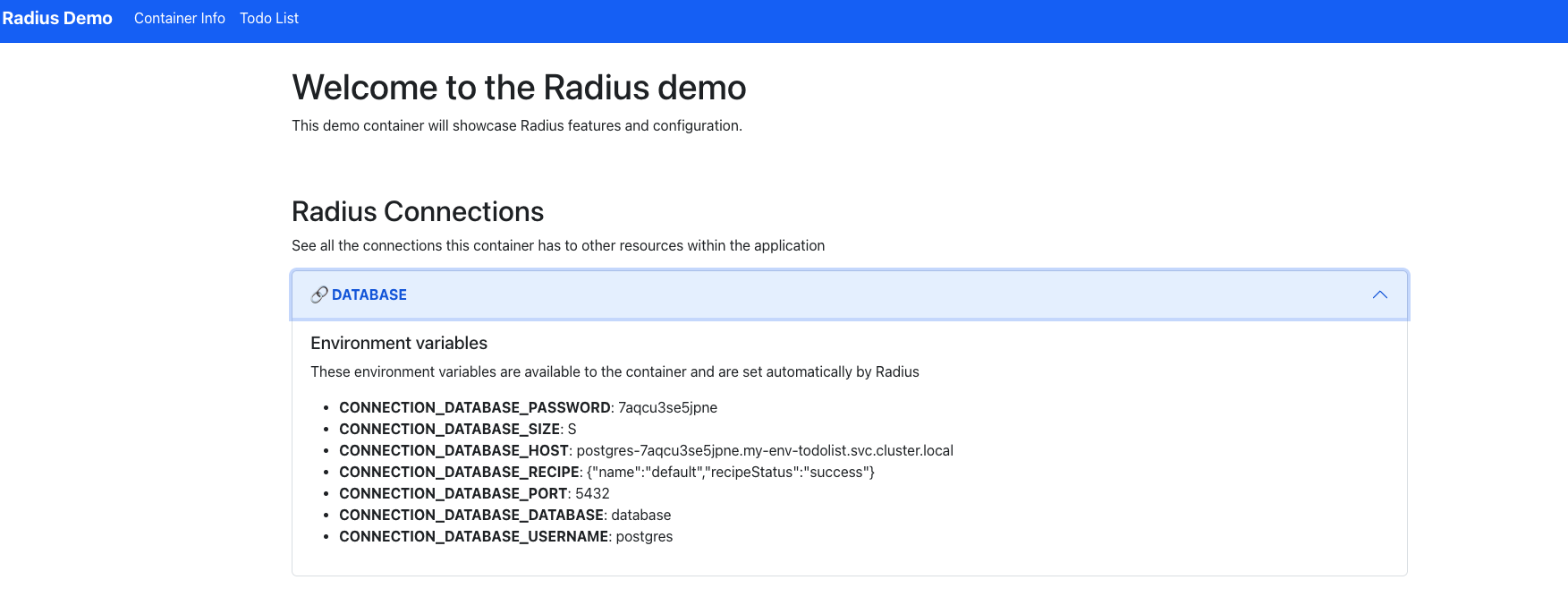
When you’re done press CTRL + c to terminate the port forward and log stream. The application continues to be deployed.
View the Application in the Radius Dashboard
If you already set up the port-forward in part 2, use the same to access the Radius Dashboard else create a new port-forward.
kubectl port-forward --namespace=radius-system svc/dashboard 7007:80
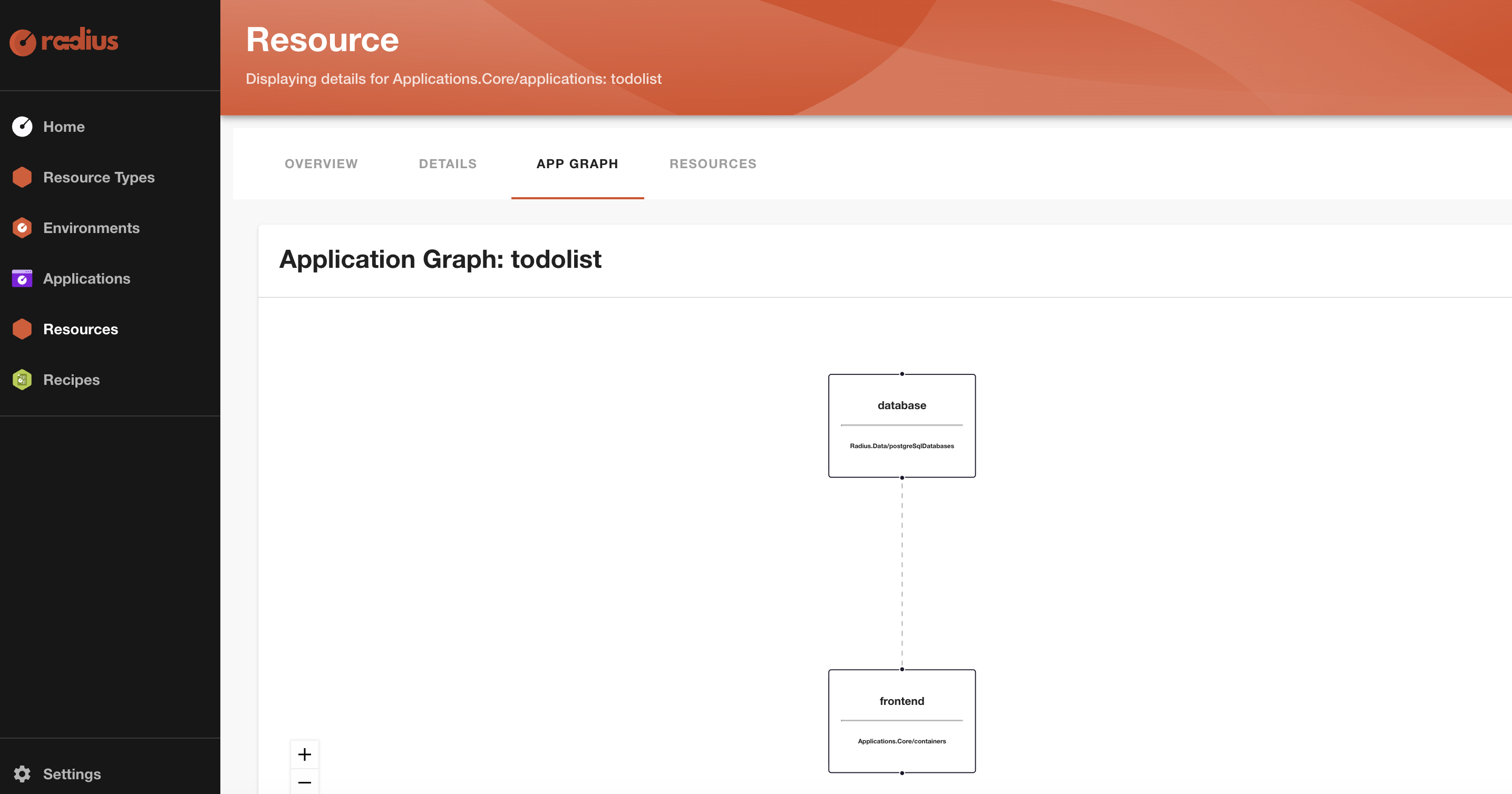
Navigate to the Radius Dashboard at http://localhost:7007, You should see a visualization of the application graph for the application, including the connection from the frontend container to database.
Cleanup
Delete the Todo List application using the rad application delete command:
rad application delete todolist
This will delete the Radius application and the deployed resources.
Optionally, uninstall Radius using the --purge flag to remove Radius and all its data from your Kubernetes cluster:
rad uninstall kubernetes --purge
Next step: Explore How-To Guides
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please feel free to star our repo and join our Discord server to stay up to date with the project.
Sorry to hear that. If you would like to also contribute a suggestion visit and tell us how we can improve.