How-To: Use Kubernetes resources in your application
Categories:
This how-to guide will provide an overview of how to:
- Leverage Kubernetes resources in your Radius Application directly.
Prerequisites
Step 1: Define the Kubernetes provider
Begin by creating a new file named app.bicep. At the top of your file, import the kubernetes provider and add its configuration. This allows you to define and deploy Kubernetes resources within Bicep.
- The
namespaceproperty determines where to deploy Kubernetes resources by default. - The
kubeConfigproperty is not currently used and can remain as an empty string (''):
@description('Specifies Kubernetes namespace for the user.')
param namespace string = 'default-demo'
extension kubernetes with {
kubeConfig: ''
namespace: namespace
}
Step 2: Add a Kubernetes secret resource
Add a Kubernetes secret to your app.bicep file. This secret will contain a small amount of sensitive data such as a password, a token, or a key:
resource secret 'core/Secret@v1' = {
metadata: {
name: 'my-secret'
}
stringData: {
'my-secret-key': 'my-secret-value'
}
}
Refer to the Kubernetes overview page for additional information about available types.
Step 3: Add a container and use the secret you just defined
Add a Radius container to your application:
// Import the set of Radius resources (Applications.*) into Bicep
extension radius
@description('The app ID of your Radius Application. Set automatically by the rad CLI.')
param application string
resource demo 'Applications.Core/containers@2023-10-01-preview' = {
name: 'demo'
properties: {
application: application
container: {
image: 'ghcr.io/radius-project/samples/demo:latest'
ports: {
web: {
containerPort: 3000
}
}
env: {
SECRET: {
value: base64ToString(secret.data['my-secret-key'])
}
}
}
}
}
Step 4: Deploy your Radius Application
Deploy your application with the rad CLI:
rad run ./app.bicep -a demo
Your console output should look similar to:
Building ./app.bicep...
Deploying template './app.bicep' for application 'demo' and environment 'default' from workspace 'default'...
Deployment In Progress...
... demo Applications.Core/containers
Deployment Complete
Resources:
demo Applications.Core/containers
Starting log stream...
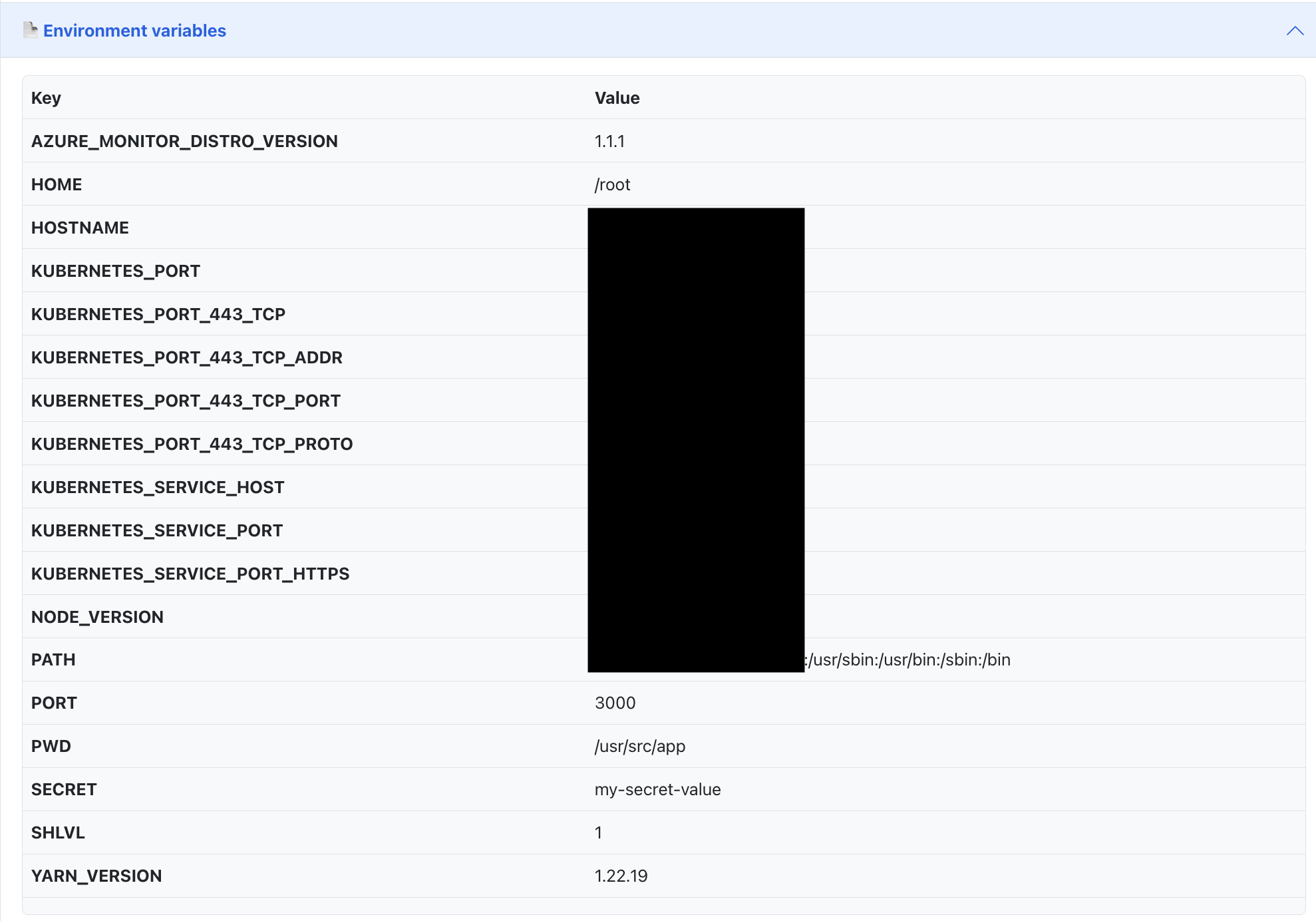
Open http://localhost:3000 to view the Radius demo container. Then navigate to the Container Metadata tab and the Environment variables section which are located near the bottom of the Radius demo webpage, there will be row dedicated to your Kubernetes secret object:
You can also prove the deployed Kubernetes secret was created by using kubectl, and running the following command with your specific secret name:
kubectl describe secret my-secret -n default-demo
Your console output should contain the following section:
Name: my-secret
Namespace: default-demo
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Type: Opaque
Data
====
my-secret-key: 15 bytes
Cleanup
To delete your Radius specific Kubernetes resources you’ll need to run:
rad app delete -a demo
Once your Radius Application has been deleted you can delete the Kubernetes Secret:
kubectl delete secret my-secret -n default-demo
Your console output should look similar to:
secret "my-secret" deleted
rad app deletedoes not delete non-Radius resources that are not directly part of a Radius Application, such as Kubernetes resources. These resources require an additional cleanup step.
Further reading
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please feel free to star our repo and join our Discord server to stay up to date with the project.
Sorry to hear that. If you would like to also contribute a suggestion visit and tell us how we can improve.